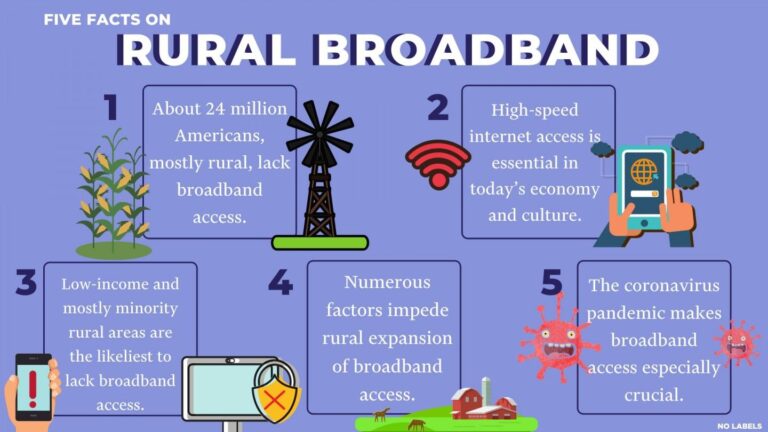
State officials are intensifying efforts to expand broadband access in rural areas, highlighting the critical need for faster, more reliable internet in underserved communities. As digital connectivity becomes increasingly essential for education, healthcare, and economic advancement, policymakers are pushing initiatives aimed at bridging the digital divide that continues to leave remote regions behind. The move comes amid growing recognition that improved rural broadband infrastructure is key to unlocking new opportunities and enhancing the quality of life for residents outside urban centers. Experts and stakeholders are calling for increased investment and innovative solutions to ensure that high-speed internet reaches even the most isolated parts of the country. [1] [3]
Table of Contents
- State Officials Emphasize Importance of Bridging the Digital Divide in Rural Areas
- Detailed Analysis of Infrastructure Challenges Hindering Rural Broadband Expansion
- Funding Strategies and Public-Private Partnerships Proposed to Accelerate Access
- Policy Recommendations Focus on Long-Term Sustainability and Community Engagement
- Concluding Remarks
State Officials Emphasize Importance of Bridging the Digital Divide in Rural Areas
State officials have reiterated the critical need to address the persistent lack of reliable internet access in rural communities, highlighting how the digital divide continues to hinder economic growth, education, and healthcare delivery. Emphasizing collaborative efforts, they called for targeted investments and innovative solutions to ensure that all residents can participate fully in the digital economy. Key priorities include expanding high-speed broadband infrastructure, fostering public-private partnerships, and leveraging federal funding opportunities to accelerate deployment.
Outlined strategies to bridge this gap involve:
- Increasing funding for rural broadband projects to stimulate infrastructure build-out
- Incentivizing internet service providers to expand coverage to underserved areas
- Implementing digital literacy programs to maximize community benefits
- Encouraging the adoption of emerging technologies such as satellite and fixed wireless
Officials underscored that closing this divide is essential not only for equitable access but also to empower rural populations with opportunities for telehealth, remote education, and modern business operations. The urgency of these initiatives reflects broader goals to enhance statewide connectivity and ensure no community is left offline in an increasingly digital world.
Detailed Analysis of Infrastructure Challenges Hindering Rural Broadband Expansion
Rural broadband expansion faces meaningful hurdles rooted in the physical and economic realities of serving sparsely populated areas. The existing infrastructure in many rural regions is often outdated or nonexistent, forcing service providers to invest heavily in long-distance fiber optic cables and wireless towers without guarantee of sufficient subscriber base to recoup costs. Additionally, challenging terrains such as mountains and dense forests complicate installation and maintenance efforts, driving up expenses. These factors culminate in service gaps where communities remain disconnected, underscoring the need for innovative infrastructure solutions that balance cost-efficiency with complete coverage.
Financial and regulatory barriers compound these technical challenges. Limited competition in rural markets frequently enough leads to reduced investment incentives for private companies. Moreover, the high upfront capital required to deploy broadband networks in isolated areas necessitates sustained public-private partnerships and targeted federal or state funding initiatives. Stakeholders must navigate complex permitting processes and inter-agency coordination, which frequently delay project timelines. Pressure is mounting on policymakers to streamline these procedures and prioritize digital inclusivity as a foundational public utility, essential for economic development and equitable access to education, healthcare, and government services.
- Outdated or absent physical infrastructure in rural communities
- Geographical and environmental challenges increasing deployment costs
- High capital investment with delayed ROI for providers
- Regulatory complexities impeding swift project implementation
- Limited competition reducing investment incentives
Funding Strategies and Public-Private Partnerships Proposed to Accelerate Access
State officials are championing a multifaceted approach to overcome the financial barriers hindering rural broadband expansion. Central to these efforts are innovative funding strategies that blend federal grants, state appropriations, and private sector investments.By harnessing a combination of public funds and private capital, the plan aims to reduce the upfront costs for infrastructure deployment in underserved areas. Officials emphasize the importance of leveraging existing federal programs while advocating for increased state-level funding to ensure sustained investment. This approach is designed to deliver faster, more reliable internet access to rural communities that have long been disconnected.
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are identified as a crucial mechanism to accelerate deployment timelines and share risks. These collaborations bring together telecommunications companies, local governments, and state agencies to co-develop networks that serve both economic and social goals. Key strategies include:
- Shared infrastructure projects to lower costs and avoid duplication.
- Performance-based contracts that incentivize rapid buildout and quality service.
- Community engagement initiatives ensuring solutions are tailored to specific local needs.
By fostering these alliances, officials anticipate not only expanding coverage but also improving long-term broadband sustainability and affordability for rural residents.
Policy Recommendations Focus on Long-Term Sustainability and Community Engagement
State officials emphasize that expanding rural broadband must prioritize long-term viability to avoid short-lived fixes that leave communities underserved. Policymakers advocate for investment in durable infrastructure capable of adapting to evolving technologies and increasing demand. This approach includes supporting public-private partnerships that combine local knowledge with private sector innovation, ensuring broadband networks remain resilient and scalable. Furthermore, officials stress the importance of allocating funds not only for initial deployment but also for continuous maintenance and upgrades, which are critical to sustaining reliable service in often remote and challenging areas.
Engaging local communities is equally vital, with policymakers recommending inclusive decision-making processes to tailor solutions to specific regional needs. This involves:
- Regular consultation with residents and businesses to identify priority areas and barriers.
- Developing training programs to improve digital literacy and maximize broadband benefits.
- Encouraging community ownership models to foster accountability and trust.
Such strategies aim to empower rural populations, enhance adoption rates, and ensure that broadband expansion efforts contribute meaningfully to local economic growth and social connectivity over time.
Concluding Remarks
As state officials continue to push for expanded rural broadband access, communities stand at the threshold of a new era of connectivity and chance. Bridging the digital divide remains a critical priority to ensure that residents in rural areas can fully participate in the modern economy, education, and healthcare. The coming months will be pivotal in determining how effectively policymakers and stakeholders collaborate to turn these broadband expansion plans into tangible benefits for rural Americans. With ongoing support and targeted investments, the hope is that faster, more reliable internet will soon become a reality for those who need it most.