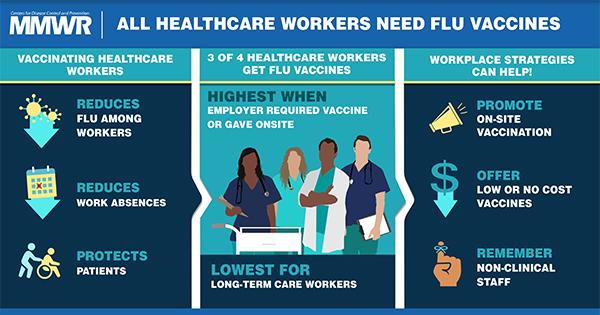
The introduction to the article could be:
Mandatory vaccination policies for healthcare workers have ignited a heated debate across the medical community and the public. As governments and institutions push for compulsory immunization to safeguard patients and curb the spread of infectious diseases, questions arise over personal freedoms, legal implications, and ethical responsibilities. With healthcare workers on the front lines, the clash between public health priorities and individual rights is more pronounced than ever, fueling intense discussions on the necessity and impact of these mandates.
Table of Contents
- Mandatory Vaccination Policies Challenge Healthcare Ethics and Worker Rights
- Examining the Impact of Vaccine Mandates on Healthcare Staffing and Patient Safety
- Healthcare Institutions Navigate Legal and Regulatory Complexities
- Best Practices for Implementing Vaccine Requirements While Maintaining Workforce Morale
- Key Takeaways
Mandatory Vaccination Policies Challenge Healthcare Ethics and Worker Rights
Healthcare institutions enforcing mandatory vaccination policies are igniting intense discussions on ethics and individual rights within the medical community. While these policies aim to safeguard patient health and prevent outbreaks, many healthcare workers argue they infringe on personal autonomy and informed consent. Critics emphasize that compelling vaccinations through obligatory measures raises questions about trust between employers and staff, potentially straining workplace morale and leading to legal challenges.
The debate also highlights broader implications for healthcare ethics, including:
- The balance between public safety and individual freedom
- Potential disparities in how mandates affect different demographics of workers
- Legal precedents concerning employment rights and medical mandates
As institutions weigh the compulsory nature of these rules, they must navigate complex questions about fairness, protection, and the limits of authority in healthcare environments.
Examining the Impact of Vaccine Mandates on Healthcare Staffing and Patient Safety
Healthcare institutions enforcing vaccine mandates for employees face a complex balancing act between ensuring patient safety and maintaining adequate staffing levels. While vaccination is a proven method to reduce the transmission of infectious diseases among vulnerable populations, some staff members have expressed concerns over personal choice and potential side effects, leading to staff shortages in certain facilities. These shortages can strain resources, increase workloads, and potentially compromise the quality of patient care during critical times.
Despite these challenges,public health experts emphasize the importance of vaccination in protecting both patients and healthcare workers in clinical settings. Key advantages cited by proponents include:
- Substantial reduction in healthcare-associated infections
- Increased trust among patients regarding their safety
- Long-term sustainability of healthcare operations by minimizing outbreak-related disruptions
As vaccine mandates continue to spark debate, finding strategies that accommodate staff concerns while prioritizing patient welfare remains at the forefront of healthcare policy discussions.
Healthcare Institutions Navigate Legal and Regulatory Complexities
Healthcare institutions across the nation are grappling with a complex web of legal and regulatory mandates as they implement mandatory vaccination policies for their staff.These organizations must carefully balance public health imperatives with employment laws, navigating evolving government directives that vary by region. The challenge is further compounded by concerns over employees’ rights, potential exemptions, and the risk of litigation, forcing hospital administrators and legal teams to consult extensively with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance while maintaining workforce stability.
Key considerations confronting healthcare providers include:
- Adherence to federal and state regulations that define the scope and enforcement of mandatory vaccination policies.
- Legal protections for employees claiming medical or religious exemptions.
- Strategies to mitigate employee pushback without compromising patient safety.
- Documentation and reporting requirements crucial for auditing and regulatory inspections.
As the policies remain subject to rapid legislative changes and judicial scrutiny, institutions are adopting flexible approaches and ongoing legal review mechanisms to adapt to this contentious public health landscape.
Best Practices for Implementing Vaccine Requirements While Maintaining Workforce Morale
Healthcare institutions aiming to balance mandatory vaccine policies with staff engagement should prioritize transparent communication and inclusive decision-making. Clearly explaining the scientific rationale behind vaccine requirements, including data on efficacy and safety, can foster trust and reduce resistance. Organizations must also provide accessible resources and forums where employees can express concerns and receive evidence-based answers. Supporting staff through flexible scheduling for vaccinations and paid leave for potential side effects demonstrates respect and encourages compliance without resentment.
Key strategies for maintaining morale include:
- Emphasizing shared goals of patient safety and public health.
- Offering incentives rather than penalties, such as recognition programs or wellness benefits.
- Providing tailored educational sessions to address misinformation and cultural sensitivities.
- Ensuring leadership models compliance and empathy to reinforce commitment.
By blending clear policies with empathetic leadership and strong communication, healthcare providers can uphold vaccination standards while nurturing a motivated and cooperative workforce.[2]
Key Takeaways
As the debate over mandatory vaccination for healthcare workers continues, the balance between public health priorities and individual rights remains central. With authorities emphasizing the critical role of vaccines in protecting vulnerable populations, opponents raise concerns about personal choice and workplace freedom. How this contentious issue will be resolved remains to be seen, but its implications are likely to shape the future of healthcare policy and practice nationwide.