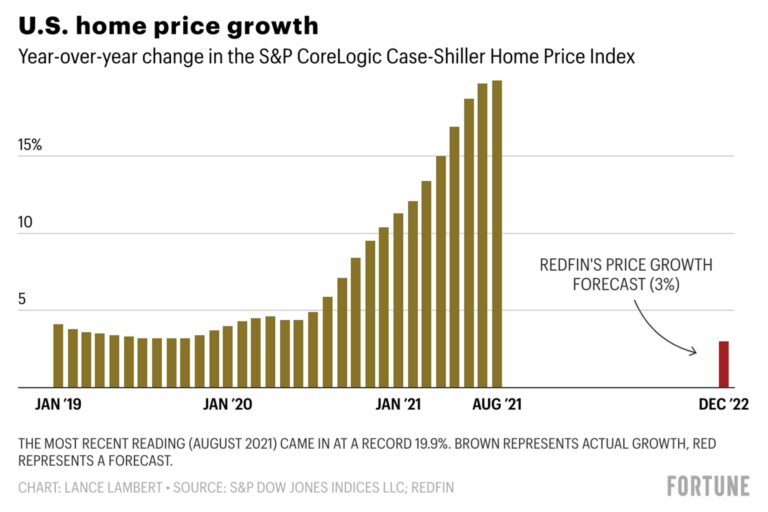
The housing market, a critical pillar of the economy, continues to evolve amid varying economic conditions, government policies, and shifting consumer preferences. Recent trends in housing demand, pricing, and construction activity are not only shaping the real estate landscape but also influencing broader economic growth. As cities grapple with supply constraints and affordability challenges, the ripple effects extend to employment, consumer spending, and investment patterns. This article delves into the latest housing market trends and examines their notable impact on economic performance and future growth prospects.
Table of Contents
- Housing Market Fluctuations and Their Ripple Effects on National Economies
- Rising Home Prices and Affordability Challenges Shaping Consumer Behavior
- The Role of Housing Investment in Driving Job Creation and Urban Development
- Policy Recommendations for Stabilizing Housing Markets and Promoting Sustainable Growth
- In Retrospect
Housing Market Fluctuations and Their Ripple Effects on National Economies
Economic landscapes are substantially shaped by shifts in the housing market, which serve as both a barometer and driver of national financial health. When property values rise, consumer confidence and spending typically increase, sparking growth in retail, construction, and service industries. Conversely, housing downturns can trigger a contraction in consumer wealth, leading to reduced expenditure and tighter credit conditions. This cyclical dynamic highlights the housing sector’s role in influencing employment rates, investment flows, and government tax revenues, which collectively cascade through the broader economy.
- Financial Sector Sensitivity: Fluctuations affect mortgage lending,impacting bank stability and credit availability.
- Consumer Behavior: Property price volatility alters household spending patterns and saving priorities.
- Government Fiscal Policy: Changes in real estate taxes and housing incentives adjust public finances and economic stimulus strategies.
Moreover, ripple effects extend beyond direct financial implications, influencing social mobility and urban development patterns. Sharp market corrections can exacerbate inequalities, limiting access to affordable housing and intensifying socio-economic divides. Policymakers face the challenge of balancing growth while ensuring market stability and inclusiveness,often relying on regulatory interventions and targeted support schemes. As such, the housing market acts as a critical nexus where economic trends and social outcomes intertwine, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptive strategies to mitigate systemic risks and bolster sustainable development.
Rising Home Prices and Affordability Challenges Shaping Consumer Behavior
Housing markets worldwide are witnessing an unprecedented surge in home prices, pushing affordability to the forefront of consumer concerns. As prices escalate, many potential buyers find themselves priced out of their desired markets, triggering a shift in spending patterns and long-term financial planning. This phenomenon is not limited to first-time buyers; even established homeowners are re-evaluating their housing strategies amid soaring costs. Key consumer behavior changes include:
- Delays in home purchasing decisions to accumulate larger down payments
- Increased demand for rental properties as an option to buying
- Relocation to suburban or less expensive areas to seek affordability
- Heightened sensitivity towards interest rate fluctuations impacting mortgage costs
The ripple effects extend beyond individual households, influencing broader economic dynamics. Elevated housing costs constrain disposable income, which in turn dampens consumption across other sectors such as retail and leisure. Moreover, the intensified focus on housing affordability is compelling financial institutions and policymakers to innovate new solutions, from flexible lending practices to expanded public housing initiatives. The intersection of rising home prices and consumer adaptation unmistakably shapes the trajectory of economic growth, demanding continuous attention from economists and stakeholders.
The Role of Housing Investment in Driving Job Creation and Urban Development
Housing investment consistently serves as a basic engine for job creation, spanning diverse sectors such as construction, real estate services, and home furnishing industries. By channeling capital into residential development projects, urban centers witness a surge in employment opportunities not only in direct construction roles but also in ancillary fields like architecture, engineering, and logistics. This dynamic generates a ripple effect-stimulating local businesses and increasing household incomes, which further invigorates consumer spending and strengthens regional economies.
Beyond immediate employment, strategic investment in housing catalyzes broader urban development by fostering infrastructure improvements and elevating neighborhood attractiveness. Modern housing developments stimulate urban renewal initiatives, encouraging the extension of transportation networks, enhancement of public amenities, and creation of vibrant community spaces. Key drivers fueling this synergy include:
- Increased demand for professional services related to urban planning and surroundings design.
- Promotion of mixed-use developments, blending residential, commercial, and cultural facilities.
- Revitalization of underserved areas, reducing economic disparities and boosting property values.
As cities evolve through sustained housing investments, the interplay between job creation and urban transformation becomes a pivotal factor shaping long-term economic resilience and growth.
Policy Recommendations for Stabilizing Housing Markets and Promoting Sustainable Growth
To foster market stability and sustainable growth, policymakers must prioritize a multi-faceted approach that balances supply expansion with demand management. Key strategies include:
- Increasing affordable housing stock through public-private partnerships and streamlined development approvals to meet growing demand without inflating prices.
- Implementing targeted demand-side measures such as housing subsidies for lower-income groups and restrictions on speculative investments to curb excessive price volatility.
- Enhancing openness and data availability to enable informed decision-making by stakeholders and reduce information asymmetry in housing markets.
In addition, sustainable urban planning and environmental considerations must be integrated into housing policies to ensure long-term resilience. This involves:
- Promoting green building standards and energy-efficient designs to reduce the ecological footprint of new developments.
- Encouraging transit-oriented development to lower transportation costs and promote efficient land use.
- Supporting inclusive community development by incorporating social infrastructure, such as schools and healthcare, to improve residents’ quality of life and economic opportunities.
In Retrospect
As housing market trends continue to evolve, their influence on broader economic growth remains profound and multifaceted. Policymakers, investors, and consumers alike must stay vigilant, recognizing that shifts in real estate dynamics can signal wider economic changes ahead. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating future opportunities and challenges,ensuring that housing markets contribute positively to sustainable economic development. The coming months will be pivotal in observing how these patterns unfold and shape the economic landscape.