The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) faces a crucial juncture as it navigates its fiscal challenges amid a recently approved $3.24 billion budget for fiscal year 2026. Despite efforts to narrow a important operating deficit-from $307 million in 2025 to a projected $168 million in 2026-the agency continues to grapple with financial pressures underscored by a potential $700 million budget gap reported last year. The Commonwealth’s dedication of $8 billion to transportation in its FY2026 budget, alongside supplemental funding sourced from the Fair Share surtax on high incomes, marks a strategic attempt to stabilize and fortify the MBTA’s operations moving forward. This review explores the MBTA’s current financial health,the impact of recent budgetary measures,and the outlook for its future fiscal stability and service delivery [[1]][[2]][[3]].
Table of Contents
- Current Revenue Streams and Expenditure Patterns Revealed
- Impact of Recent Policy Changes on MBTA Financial Stability
- Challenges Facing Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
- Strategic Recommendations for Enhancing Budget Efficiency and Growth
- Final Thoughts
Current Revenue Streams and Expenditure Patterns Revealed
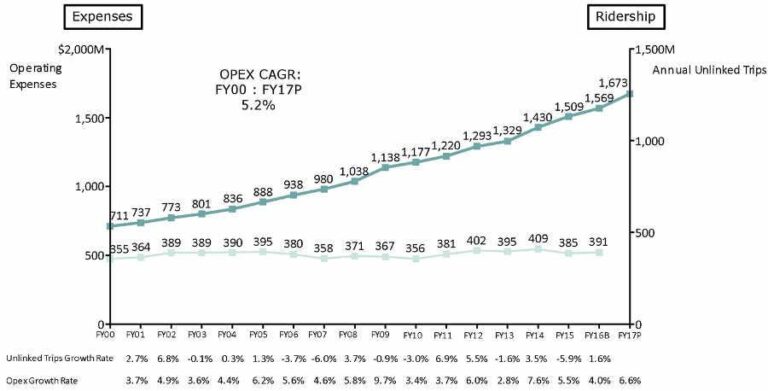
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) derives its revenue primarily from three key sources: fares collected from riders, government subsidies, and ancillary income streams such as advertising and property leases. Farebox recovery rates have shown a cautious uptick post-pandemic, reflecting gradual ridership recovery; though, subsidies remain the backbone of the budget, underscoring ongoing reliance on state and federal funding to cover operational costs.Additional income, while smaller in scale, provides crucial supplementary cash flow through commercial partnerships and real estate holdings.
In terms of expenditure, the MBTA’s largest outlays focus on maintenance, capital improvements, and personnel costs. Recent spending patterns reveal a strategic shift towards upgrading aging infrastructure, indicating prioritization of long-term sustainability over short-term repairs.Operating expenses also include significant allocations for safety enhancements and service expansions, reflecting the authority’s commitment to improving rider experience. Together, these elements outline a financial picture balanced delicately between immediate operational demands and future readiness.
Impact of Recent Policy Changes on MBTA Financial Stability
The recent policy adjustments have introduced both challenges and opportunities for the MBTA’s fiscal landscape. Key changes in funding formulas and fare restructuring have resulted in a recalibration of revenue streams,affecting operational budgets across multiple departments. While increased subsidies from state allocations provide a temporary cushion, uncertainties in federal support and inflationary pressures on maintenance costs continue to strain resources. Critical financial indicators reveal a gap between projected income and expenditures, urging a reassessment of spending priorities.
- Revised fare policies have led to fluctuating ridership and revenue consistency.
- State funding realignments aim to support capital projects but limit discretionary spending.
- Inflation and labor cost increases intensify operational budget shortfalls.
- Debt management strategies are being reviewed to maintain bond ratings and financial credibility.
These policy shifts underscore the urgency for strategic financial planning moving forward. Balancing service quality with fiscal responsibility demands innovative approaches to cost-control and revenue enhancement. The MBTA’s leadership faces mounting pressure to implement obvious, data-driven budget frameworks. This environment fosters a climate where long-term sustainability hinges not only on legislative support but also on adaptive management and stakeholder engagement to navigate an evolving economic landscape.
Challenges Facing Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
The MBTA faces a complex landscape of financial hurdles that threaten its long-term viability. Key pressures include escalating pension and healthcare obligations for retired employees, which continue to place a heavy burden on the agency’s annual budget. Additionally, fluctuating ridership patterns, exacerbated by remote work trends and changing commuter behaviors, have contributed to unpredictable revenue streams. These factors make accurate forecasting challenging and hinder the authority’s ability to plan capital investments with confidence.
Critical issues demanding attention include:
- Rising operational costs driven by aging infrastructure and necessary system upgrades
- Dependence on unpredictable state and federal funding sources
- Balancing fare adjustments without alienating riders or reducing accessibility
Addressing these multifaceted challenges will require innovative fiscal strategies and sustained political commitment. Without significant reforms and investment prioritization, the MBTA risks facing deeper deficits that could compromise service reliability and system modernization goals.
Strategic Recommendations for Enhancing Budget Efficiency and Growth
To fortify the MBTA’s financial foundation, a multifaceted approach emphasizing operational efficiency and innovative funding avenues is crucial. Priority should be given to optimizing resource allocation through rigorous performance metrics and data-driven decision-making. This includes streamlining maintenance schedules to reduce downtime, renegotiating vendor contracts for cost savings, and leveraging technology to automate ticketing and customer service processes. Equally crucial is pursuing alternative revenue streams, such as public-private partnerships, dynamic pricing models for peak travel times, and enhanced real estate advancement around transit hubs.
Enhancing budget growth demands a strategic focus on long-term sustainability paired with community engagement. Implementing transparent budgeting processes and regular stakeholder consultations will build public trust and support for necessary fare adjustments or capital investments. Moreover, targeting grants and federal funding opportunities aligned with environmental and infrastructure initiatives can unlock critical financing. Key action points include:
- Integrating smart transit solutions to reduce operational waste and enhance rider experience.
- Establishing a robust performance audit framework to continuously identify inefficiencies.
- Fostering cross-agency collaborations to share resources and streamline project delivery.
Final Thoughts
As the MBTA navigates the complexities of its budget,the balance between fiscal responsibility and maintaining essential services remains pivotal. Ongoing assessments and transparent financial strategies will be critical in shaping the future of Boston’s primary transit system. Stakeholders and commuters alike will be watching closely to see how the authority manages resources to ensure a sustainable and efficient transportation network moving forward.