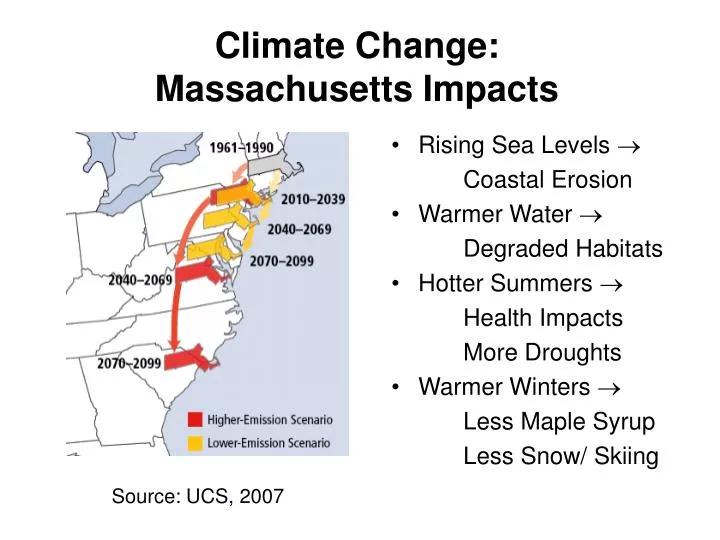
Climate change is increasingly posing a serious threat to the health of Massachusetts residents, as rising carbon dioxide levels and shifting environmental conditions accelerate. Human activities have elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide by 50% in less than two centuries, intensifying global warming and triggering a cascade of health risks from heat waves to worsening air quality. As sea levels rise and weather patterns become more extreme, public health officials in Massachusetts face mounting challenges in safeguarding their communities against this sprawling crisis [[1]]([[2]]).
Table of Contents
- Climate Change Escalates Health Risks Across Massachusetts
- Rising Temperatures Drive Surge in Respiratory and Heat-Related Illnesses
- Vulnerable Communities Face Disproportionate Impact From Environmental Hazards
- Public Health Officials Call for Urgent Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
- Wrapping Up
Climate Change Escalates Health Risks Across Massachusetts
Massachusetts is witnessing an alarming surge in health threats tied directly to the escalating climate crisis.Rising levels of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases have not only driven temperature increases but have also intensified the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. These environmental shifts are amplifying risks such as heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems from poor air quality, and the spread of vector-borne diseases. Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions, face disproportionate impacts, straining public health resources across the state.
Health professionals and researchers point to several immediate challenges confronting Massachusetts residents:
- Increased heat waves: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can trigger heatstroke and exacerbate cardiovascular diseases.
- Degraded air quality: Elevated ozone and particulate matter worsen asthma and other respiratory ailments.
- Expanding range of infectious diseases: Warmer climates allow ticks and mosquitoes to thrive longer,spreading Lyme disease and West Nile virus.
These evolving conditions underscore the urgent need for integrated strategies that address both climate mitigation and adaptive healthcare measures to protect communities statewide.
Rising Temperatures Drive Surge in Respiratory and Heat-Related Illnesses
As average temperatures continue to climb across Massachusetts, public health officials are reporting a noticeable rise in respiratory and heat-related illnesses. The state’s vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with chronic respiratory conditions, are experiencing more frequent emergency room visits during prolonged heatwaves. Elevated temperatures exacerbate air pollution and increase the concentration of allergens like pollen, triggering severe asthma attacks and other breathing difficulties.Hospitals face added strain as carbon monoxide poisonings and heat exhaustion cases spike during extreme heat events, highlighting urgent needs for adaptive measures in healthcare systems.
Key health impacts linked to rising temperatures include:
- Heightened cases of heat stroke and dehydration, notably during summer months.
- Surges in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) flare-ups due to polluted air.
- Increased hospitalizations for cardiovascular stress related to heat exposure.
- Worsening of respiratory symptoms tied to longer allergy seasons and intensified ground-level ozone.
Experts emphasize that without aggressive efforts to mitigate climate change and bolster community resilience, these health threats will continue to escalate, placing further pressure on Massachusetts’ healthcare infrastructure.
Vulnerable Communities Face Disproportionate Impact From Environmental Hazards
Massachusetts’ most vulnerable populations-including low-income families, elderly residents, and communities of color-bear a disproportionate brunt of environmental hazards exacerbated by climate change. These groups are often situated in neighborhoods with older infrastructure, limited green space, and proximity to industrial pollution, making them more susceptible to the harmful effects of heat waves, air pollution, and flooding. The physical and mental toll is compounded by limited access to healthcare and social services,creating a cycle of increased health risks and diminished resilience.
Key factors contributing to this disparity include:
- Higher exposure to extreme weather events like hurricanes and heatwaves without adequate cooling or shelter options.
- Pre-existing health conditions such as asthma that are aggravated by worsening air quality.
- Economic barriers that limit the ability to prepare for or recover from environmental disasters.
As climate threats intensify, addressing these vulnerabilities through targeted policies and investment in community infrastructure is critical to safeguarding the health of Massachusetts’ most at-risk residents.
Public Health Officials Call for Urgent Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Massachusetts public health officials have issued a clarion call for immediate and robust climate action, emphasizing that the state’s growing health threats cannot be ignored. Rising temperatures, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and deteriorating air quality are converging to strain healthcare systems and exacerbate vulnerabilities among at-risk populations, including the elderly, children, and individuals with respiratory conditions. Experts underscore the urgent need to integrate climate adaptation measures into public health planning, ensuring communities are better prepared to withstand heatwaves, vector-borne diseases, and flooding-related hazards.
Key strategies advocated include:
- Expanding early warning systems for heat and air pollution
- Enhancing urban green spaces to mitigate heat island effects
- Strengthening healthcare infrastructure to manage climate-exacerbated illnesses
- Targeted public education campaigns focusing on climate-related health risks
These initiatives are critical to reducing the future burden on Massachusetts’ public health resources and safeguarding the well-being of all residents.Officials warn that without swift mitigation efforts, including aggressive greenhouse gas reductions and community resilience investments, the state’s health outlook will continue to worsen in the face of climate change’s mounting impact.
Wrapping Up
As the evidence mounts, the growing threat of climate change to Massachusetts’ health is undeniable. Rising temperatures, increased air pollution, and more frequent extreme weather events are not only reshaping the environment but also placing residents’ well-being at meaningful risk. Addressing these challenges requires urgent action from policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities alike to mitigate harm and build resilience. The health of Massachusetts hangs in the balance as the climate crisis accelerates,underscoring the imperative for comprehensive and sustained efforts to protect its people and future generations.For more on how carbon dioxide and climate change are affecting our planet and health, visit NASA’s Climate Change resources[[1]](https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/carbon-dioxide/?intent=121).