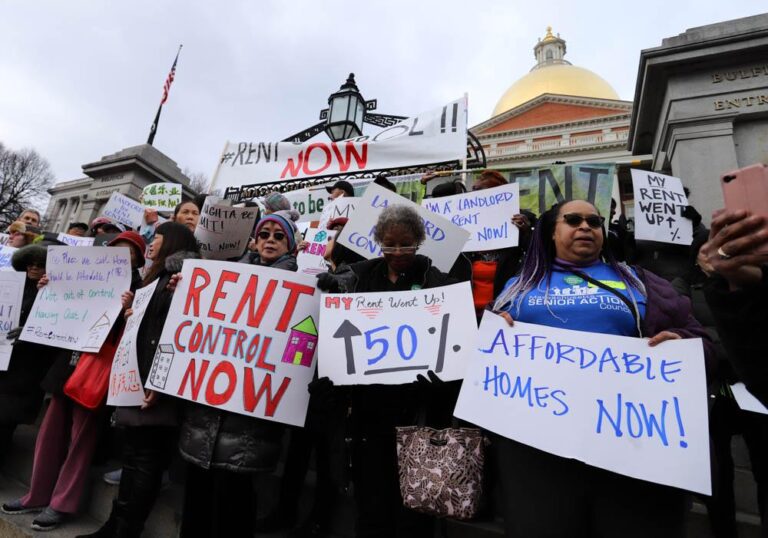Boston is at the centre of a heated debate over rent control as city officials and stakeholders weigh the potential reintroduction of policies to cap rent prices. After nearly three decades as Massachusetts repealed statewide rent control in 1994, the Boston City Council recently passed a proposal backed by the mayor aimed at curbing rising housing costs and preventing homelessness.The renewed push for rent regulation reflects growing concerns over affordability amid escalating rents,but it also faces fierce opposition from business leaders and landlords worried about the economic impact. As Boston wrestles with the complexities of balancing tenant protections and market realities, the outcome of this debate could reshape the city’s housing landscape in profound ways. [2] [3] [1]
Table of Contents
- Boston’s Housing Crisis Sparks Renewed Interest in Rent Control Measures
- Analyzing the Economic and Social Impacts of Rent Regulation in Urban Areas
- Voices from the Community: Landlords, Tenants, and Advocates Weigh In
- Policy Pathways Forward: Crafting Balanced Solutions for Boston’s Rent Challenges
- Future Outlook
Boston’s Housing Crisis Sparks Renewed Interest in Rent Control Measures
As Boston grapples with escalating housing costs and limited rental inventory, city leaders and advocates have reignited discussions on rent control as a potential tool to stabilize the rental market. Earlier this year, the Boston City Council and Mayor Michelle Wu advanced a local measure permitting a form of rent control, aiming to protect tenants from rapid monthly rent increases. However, this proposal, along with several related bills, ultimately stalled at the state legislature, reflecting ongoing contention surrounding the policy’s viability within Massachusetts’ broader regulatory framework.Supporters emphasize the urgency of mitigating displacement risks and providing long-term affordability amid a worsening housing shortage.
Key arguments fueling the debate include:
- Advocates: Highlight rent control as essential for tenant protection and community stability.
- Opponents: Warn that rent control discourages housing growth and may reduce overall availability.
- State Context: Massachusetts banned rent control statewide in 1994, a ban that still governs policy despite local efforts to reconsider.
Despite resistance from powerful business groups and chambers of commerce branding rent control a “terrible idea,” the ongoing housing crisis keeps rent regulation at the forefront of city policy conversations, with many stakeholders urging renewed legislative action to address urgent affordability concerns.
Analyzing the Economic and Social Impacts of Rent Regulation in Urban Areas
Economic analyses of rent regulation reveal a complex web of consequences that ripple through urban housing markets. While proponents argue that rent control provides stability and financial relief for tenants in high-cost cities like Boston, critics highlight the risk of reduced investment in new housing developments and a potential decline in property maintenance. Economists warn that strict rent caps can lead to housing shortages as landlords find diminished incentive to upgrade or expand rental portfolios, ultimately exacerbating affordability issues rather than alleviating them.
The social fabric of regulated urban areas also undergoes notable shifts.Rent regulation can foster community retention, helping long-term residents avoid displacement amid rising market pressures, which benefits neighborhood diversity and social cohesion. However, it may simultaneously produce unintended consequences such as reduced mobility and a mismatch between available units and renter needs. Key considerations include:
- Perhaps limiting access for new residents or lower-income groups seeking housing in regulated areas
- Shaping landlord-tenant dynamics toward greater tenant security but possibly less landlord flexibility
- Influencing local economic vitality by impacting the availability and quality of rental housing stock
Voices from the Community: Landlords, Tenants, and Advocates Weigh In
Landlords express apprehension about potential rent control policies,citing concerns over financial feasibility and building maintenance. Many argue that rigid controls could:
- Limit their ability to cover rising costs such as property taxes and repairs
- Discourage investment in new rental housing
- Reduce the overall supply of quality units available to tenants
From their perspective, fostering a balanced approach that includes incentives for upkeep and development is crucial to avoid unintended consequences.
On the flip side, tenants and housing advocates emphasize the critical need for protections amid escalating rents and housing shortages. Their comments highlight:
- The growing displacement of longtime residents in diverse Boston neighborhoods
- Calls for rent stabilization measures to ensure affordability and secure living conditions
- The importance of community input in shaping policies that prioritize equitable housing access
Advocates argue that without intervention, Boston risks deepening its housing crisis, disproportionately affecting low- and moderate-income families.
Policy Pathways Forward: Crafting Balanced Solutions for Boston’s Rent Challenges
In navigating Boston’s complex rent landscape, policymakers are weighing nuanced strategies that align sustainable rentals with community equity.Innovators suggest a multi-faceted approach, combining targeted rent stabilization for vulnerable populations with incentives that spur affordable housing development. This includes expanding tax credits for landlords who maintain reasonable rents and integrating public-private partnerships to alleviate pressure on the housing market.Stakeholders emphasize that purely stringent rent control, without complementary policies, risks discouraging investment and reducing overall housing supply - a balance of protections and growth is essential for long-term viability.
Emerging frameworks also call for enhanced tenant support programs to empower renters facing displacement. These may encompass:
- Legal aid services to improve negotiating power and dispute resolutions.
- Rental assistance funds targeted during economic downturns or crises.
- Community land trusts aimed at preserving affordability through collective ownership.
Such initiatives, combined with data-driven zoning reforms, offer a promising template for crafting a fair yet flexible housing surroundings, where the needs of both residents and property owners are recognized. The evolving discourse signals a growing consensus that Boston’s rent challenges demand innovation beyond traditional rent control measures.
Future Outlook
As the rent control debate continues to unfold in Boston and across Massachusetts, the path forward remains uncertain. Advocates push for measures to ease the burden on renters, while business leaders warn of potential unintended consequences. With a statewide ballot measure potentially in play for 2026, this contentious issue is likely to remain at the forefront of housing policy discussions in the coming months. Stakeholders from all sides will be watching closely as the conversation evolves, seeking solutions to balance affordability with economic growth in the region[[[1]](https://www.bostonherald.com/2025/08/11/massachusetts-rent-control-push-greater-boston-chamber-ceo-calls-measure-terrible-idea/),[[[2]](https://www.boston.com/real-estate/real-estate/2025/08/06/rent-control-could-be-on-the-ballot-in-2026/),[[[3]](https://www.wbur.org/news/2025/07/29/mass-rent-control-housing-advocacy).